Section: New Results
Applications for Educational Technologies
Multi-Armed Bandits for Adaptive Personalization in Intelligent Tutoring Systems
Participants : Manuel Lopes [correspondant] , Pierre-Yves Oudeyer, Didier Roy, Alexandra Delmas, Benjamin Clement.
The Kidlearn project
Kidlearn is a research project studying how machine learning can be applied to intelligent tutoring systems. It aims at developing methodologies and software which adaptively personalize sequences of learning activities to the particularities of each individual student. Our systems aim at proposing to the student the right activity at the right time, maximizing concurrently his learning progress and its motivation. In addition to contributing to the efficiency of learning and motivation, the approach is also made to reduce the time needed to design ITS systems.
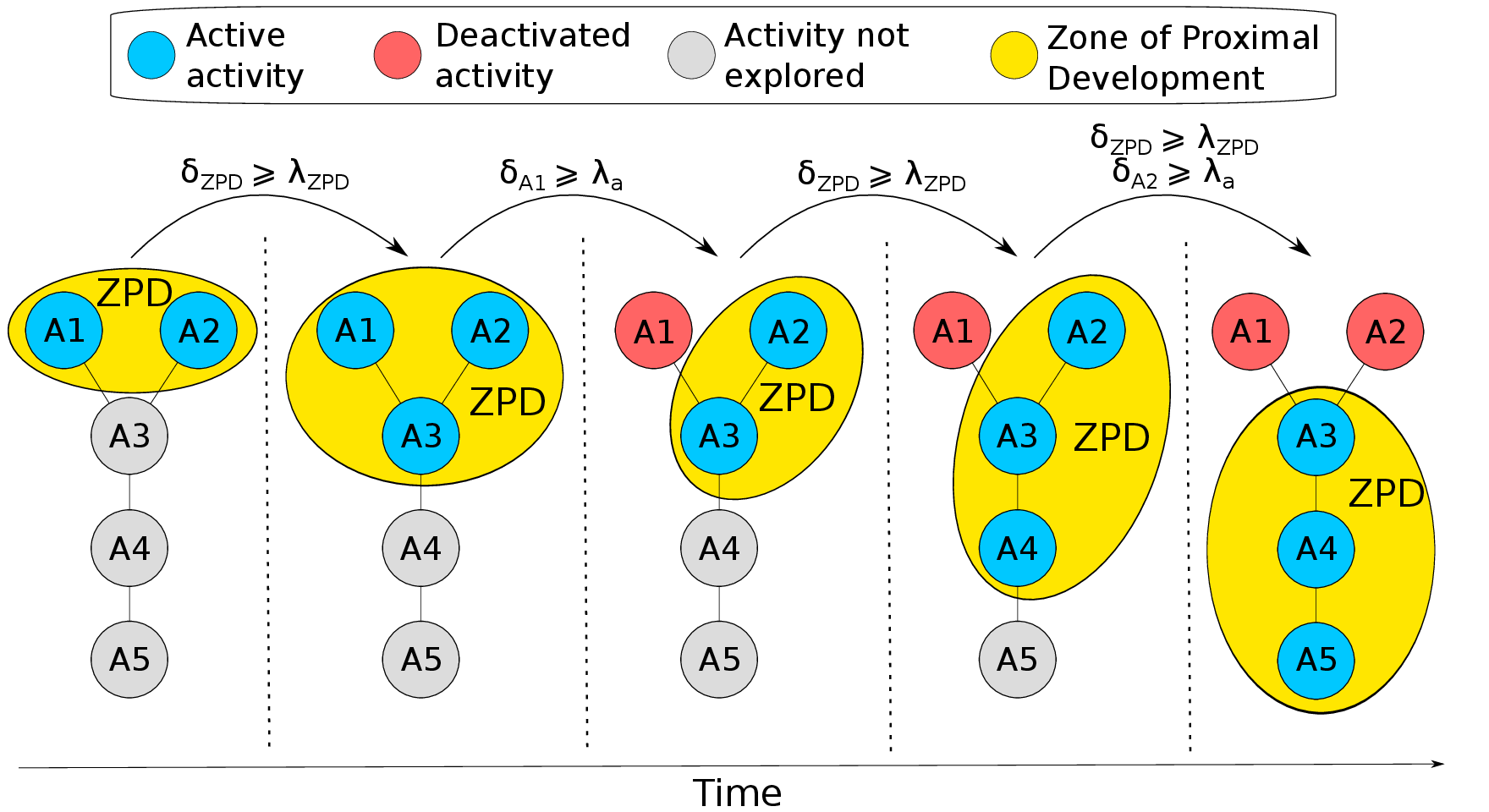
We present an approach to Intelligent Tutoring Systems which adaptively personalizes sequences of learning activities to maximize skills acquired by students, taking into account the limited time and motivational resources. At a given point in time, the system proposes to the students the activity which makes them progress faster. We introduce two algorithms that rely on the empirical estimation of the learning progress, RiARiT that uses information about the difficulty of each exercise and ZPDES that uses much less knowledge about the problem.
The system is based on the combination of three approaches. First, it leverages recent models of intrinsically motivated learning by transposing them to active teaching, relying on empirical estimation of learning progress provided by specific activities to particular students. Second, it uses state-of-the-art Multi-Arm Bandit (MAB) techniques to efficiently manage the exploration/exploitation challenge of this optimization process. Third, it leverages expert knowledge to constrain and bootstrap initial exploration of the MAB, while requiring only coarse guidance information of the expert and allowing the system to deal with didactic gaps in its knowledge. The system is evaluated in a scenario where 7-8 year old schoolchildren learn how to decompose numbers while manipulating money. Systematic experiments are presented with simulated students, followed by results of a user study across a population of 400 school children. [14]
A Comparison of Automatic Teaching Strategies for Heterogeneous Student Populations
Online planning of good teaching sequences has the potential to provide a truly personalized teaching experience with a huge impact on the motivation and learning of students. In this work we compare two main approaches to achieve such a goal, POMDPs that can find an optimal long-term path, and Multi-armed bandits that optimize policies locally and greedily but that are computationally more efficient while requiring a simpler learner model. Even with the availability of data from several tutoring systems, it is never possible to have a highly accurate student model or one that is tuned for each particular student. We study what is the impact of the quality of the student model on the final results obtained with the two algorithms. Our hypothesis is that the higher flexibility of multi-armed bandits in terms of the complexity and precision of the student model will compensate for the lack of longer term planning featured in POMDPs. We present several simulated results showing the limits and robustness of each approach and a comparison of heterogeneous populations of students.
|
This work has been publish and presented at Educational Data Mining 2016 conference in Raleigh, USA [76].
Github link of the experiments paper code : https://github.com/flowersteam/kidlearn/tree/edm2016
The KidBreath project
To create learning contents linked to asthma to personalize it like mathematics activities in Kidlearn project [14] we used recommandation criterias in Therapeutic Education Program for asthma kids made by Health High Autority. Following an approach of participatory design [114], contents were validated by medical experts like health educators, pulmonoligists and pediatrics. Then, we conducted a workshop with forty kids aged 8 in order to iterate over the application interfaces and evaluate enjoy about it with observations. Finally, we realized a focus group with 5 asthma kids to validate the global comprehension of a part of the content. It revealed that children wanted more contents about the crisis treatment and how the asthma works in the human system (verbatims).
In a preliminary study, we experimented two conditions in 20 control children (with 3 asthma kids), one giving the possibility of choosing activities like the child wants, and one no giving this choice (activities displayed in random). No significative difference between the two groups, but results showed KidBreath was easy to use with scores > 75 using System Usability Scale [115]. Based on Cordova and Lepper works to evalueate motivation and knowledge with similar system and population [121], children had their disease knowledge increased with just one week use and were motivated using it. Finally, asthma kids showed they were more engaged than healthy kids and used KidBreath more seriously (stayed in breaks). These results was presented in the 5th edition of Serious Games in Medicine Conference in Nice.
We presented Thesis project in some events this year, with one publication surbmitted and validated:
-
2nd Meeting for Aquitaine and Euskadi companies in Biology and Health Between, February 11th 2016 in San sebastian (poster),
-
Hackathon of innovation in pulmonary diseases, Respirhacktion, September 16th to 18th 2016 in Paris (project development in hackathon ),
-
5th Conference in Health Ergonomics and Patient Safety, October 5th to 7th 2016 (poster) [102],
-
Learning Lab day, November 16th in Inria Paris (oral presentation of project),
-
5th edition of Serious Games in Medicine Conference, December 2nd to 3rd 2016 in Nice Sofia-Antipolis University (oral presentation).
Poppy Education: Designing and Evaluating Educational Robotics Kits
Participants : Pierre-Yves Oudeyer [correspondant] , Didier Roy, Théo Segonds, Stéphanie Noirpoudre, Marie Demangeat, Thibault Desprez, Matthieu Lapeyre, Pierre Rouanet, Nicolas Rabault.
The Poppy Education project aims to create, evaluate and disseminate all-inclusive pedagogical kits, open-source and low cost, for teaching computer science and robotics.
It is designed to help young people to take ownership with concepts and technologies of the digital world, and provide the tools they need to allow them to become actors of this world, with a considerable socio-economic potential. It is carried out in collaboration with teachers and several official french structures (French National Education, High schools, engineer schools, ... ). For secondary education and higher education, scientific literacy centers, Fablabs.
Poppy Education is based on the robotic platform poppy (open-source platform for the creation, use and sharing of interactive 3D printed robots), including:
-
Poppy Humanoid, a robust and complete robotics platform designed for genuine experiments in the real world and can be adapted to specific user needs.
-
Poppy Torso, a variant of Poppy Humanoid that can be easily installed on any flat support.
-
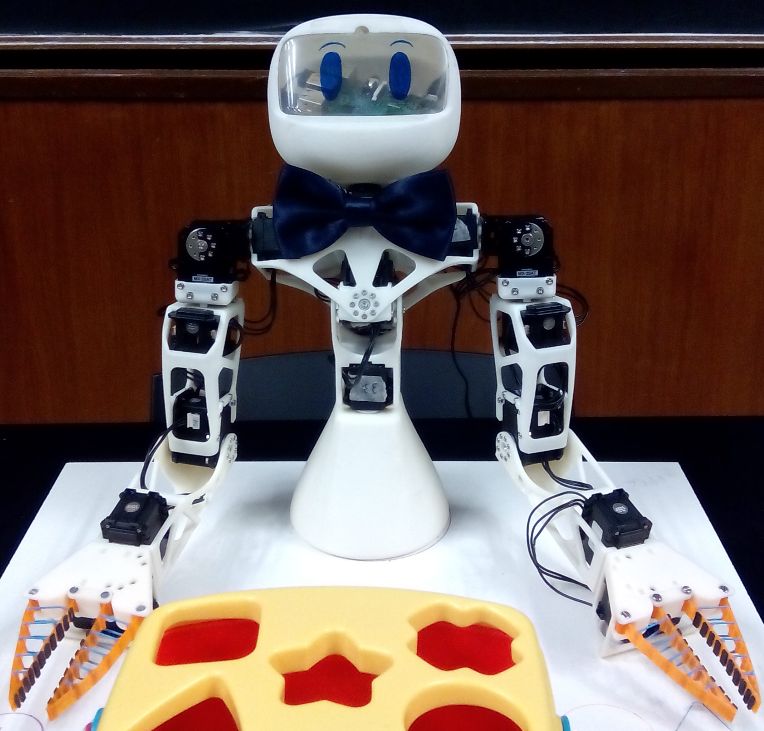
Ergo Jr, a robotic arm. Durable and inexpensive, it is perfect to be used in class. Python. Directly from a web browser, using Ipython notebooks (an interactive terminal, in a web interface for the Python Programming Language).
-
Snap. The visual programming system Snap, which is a variant of Scratch. Its features allow a thorough introduction of information technology.
-
C++, Java, Matlab, Ruby, Javascript, etc. thanks to a REST API that allows you to send commands and receive information from the robot with simple HTTP requests.
-
Virtual robots (Poppy Humanoid, Torso and Ergo) can be simulated with the free simulator V-REP. It is possible in the classroom to work on the simulated model and then allow students to run their program on the physical robot.
Pedagogical experimentations : Design and experiment robots and the pedagogical activities in classroom
This project is user centred design. The pedagogical tools of the project (real and virtual robots, pedagogical activities, etc.) are being created directly with the users and evaluated in real life by experiments. For our experimentations in the classroom we are mainly using the robot Poppy Ergo Jr (real and virutal) and Snap! Our purpose is to improve this pedagogical tools and to create pedagogical activities and resources for teachers.
-
At the beginning of the project, we established a pedagogical working group of 12 volunteers, teachers from different level (mainly high school teachers of the Aquitaine region) to help to design educational activities in line with the needs of the school curriculum and to test them in the classroom.
At the beginning of the second year of the project we added 7 other teachers from different background (middle-school and high school teachers) into the group to add more diversity.
We organised some training to help them to discover and learn how to use the robotics platform, then we met monthly to exchange about the project and to get some feedbacks from them.
You can see the videos of pedagogical robotics activities here:
https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLdX8RO6QsgB7hM_7SQNLvyp2QjDAkkzLn
-
Experiment and Evaluate the pedagogical kits:
Some engineer of the Poppy Education team went to visit the teachers in their school to see and to evaluate the pedagogical tools (robot and activities) in real contexts of use.
In addition to the observations in classroom, two trainee students of Master 2 in cognitive sciences (M. Demangeat, D. Thibaut) have established an experimental protocol to evaluate the utility and the integration of the pedagogical kits in class. They created and filled out questionnaires by teachers and students. The analyzes of the results are presented in their paper thesis.
This experimentations are helping us to understand the educational needs, to create and improve the pedagogical tools.
Partnership on education projects
-
The Arts and Métiers campus at Bordeaux-Talence in partnership with Inria wishes to contribute to its educational and scientific expertise to the development of new teaching methods and tools. The objective is to develop teaching sequences based on a project approach, relying on an attractive multidisciplinary technological system: the humanoid Inria Poppy robot.
The humanoid Inria Poppy robot offers an open platform capable of providing an unifying thread for the different subjects covered during the 3-years of the Bachelor training: mechanics, manufacturing (3D printing), electrical, mecha-tronics, computer sciences, design.
Last year student of "bachelor degree" (ENSAM-Talence) have designed, manufactured, assembled and programmed 4 different solutions to replace the fixed hand of Poppy by a gripper device:
-
Students from the BTS audiovisual of Saint-Genes La Salle have created a complete video report on the Poppy project to highlight the use in education and art:
-
Poppy entre dans la danse (Poppy enters the dance)
The project "Poppy enters the dance" (Canope 33) uses the humanoid robot Poppy, able to move and experience the dance. The purpose of this project is to allow children to understand the interactions between science and choreography, to play with the random and programmable, to experience movement in dialogue with the machine. At the beginning of the project they attended two days of training on the humanoid robot (Inria - Poppy Education). During the project, they met the choreographer Eric Minh Cuong Castaing and the engineer Segonds Theo (Inria - Poppy Education).
You can see an overview of the project with kindergarten students :
Created pedagogical documents and resources
-
Rebuilt the documentation of Poppy-project
It was necessary for us to have an accessible and clear documentation to help teachers to use and create projects with the robots in the classroom so we rebuilt the existing documentation of the robotics platform Poppy. We added and improve the contents and we used the platform gitbook :
-
The pedagogical booklet [96] brings together all the pedagogical activities and project testing in the classroom. It provides guided activities, small challenges and projects to become familiar with the Poppy Ergo Jr robot and the Programming language Snap!
https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B2jV8VX-lQHwTUxXZjF3OGxHVGM/view
The pedagogical activities are also available on the Poppy project forum where everyone is invited to comment and create new ones:
https://forum.poppy-project.org/t/liste-dactivites-pedagogiques-avec-les-robots-poppy/2305
-
Guide on the pedagogical use of the kit Poppy Ergo Jr in classroom
We wrote an article [95] to explain how to use the Robot Ergo Jr in a classroom. It includes a summary of the characteristics of the robots, activities example and give all the necessary resources:
https://pixees.fr/dans-la-famille-poppy-je-voudrais-le-robot-ergo-jr
-
Demonstration guide to introduce the project
This document is for people who already have a little experience with the Poppy Ergo Jr robot and snap! and wishing to present the project (i.e: to a colleague/acquaintance, on a exhibition stand, during a conference).
The purpose of this document is to provide the necessary elements to enable the Poppy Education project to be presented through the use of Poppy Ergo Jr. robot. The key points of the Poppy Education project and the features of Poppy Ergo Jr kit are presented as well as examples of demonstrations of educational activities (videos and snap! projects) and educational projects (videos). An example of structuring a demo is provided at the end of the document.
https://forum.poppy-project.org/t/guide-de-demo-du-kit-pedagogique-poppy-ergo-jr-version-beta/2698
-
Model of pedagogical activities sheet
We designed a model of pedagogical activity sheet. It helps us to get back the various activities and allows to have a homogeneous presentation. It is simpler to share and get back the creations of each.
https://forum.poppy-project.org/t/modele-de-fiche-pedagogique-telechargeable-pour-les-activites-robotiques/2706
Scientific mediation
To promote educational uses of the platform, we participated in events (conference, seminar etc.).
We participated as well at some workshops to introduce students to robotics and programming.
Symposium robotics
We organized a symposium robotics (http://dm1r.fr/colloque-robotique-education/) that present research results and feedback on the use of Poppy and Thymio robots in education (other robots have been discussed, such as BeeBot and Metabot), from kindergarten to higher education, The Centers for Scientific and Technical Culture.
It was a 2 day event : 200 participants, 40 speakers (conferences and workshops).
Poppy Education team and the working group teachers helped with the organisation of the event and during the event (talk and workshops).
All conference videos are available on the web :
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=prFmC-BpdY8&index=1&list=PL9T8000j7sJBC_H3L_hS-i4Ltlh1Fz2FY
IniRobot: Educational Robotics in Primary Schools
Participants : Didier Roy [correspondant] , Pierre-Yves Oudeyer.
IniRobot (a project done in collaboration with EPFL/Mobsya) aims to create, evaluate and disseminate a pedagogical kit which uses Thymio robot, open-source and low cost, for teaching computer science and robotics.
IniRobot Project consists to produce and diffuse a pedagogical kit for teachers and animators, to help to train them directly or by the way of external structures. The aim of the kit is to initiate children to computer science and robotics. The kit provides a micro-world for learning, and takes an enquiry-based educational approach, where kids are led to construct their understanding through practicing an active investigation methodology within teams. It is based on the use of the Thymio II robotic platform. More details about this projects were published in RIE 2015 [50] , which presents the detailed pedagogical objectives and a first measure of results showing that children acquired several robotics-related concepts. See also http://www.inirobot.fr.
Deployment: After 24 months of activity, IniRobot is used by about 1400 adults and 16 000 children in 54 cities of France. Example of action in university: MEEF teacher training for the hope of Aquitaine. Example of action in school: training of all Gironde Pedagogical ICT Advisors, covering nearly 1000 schools. Example of action in the extracurricular time: training 82 facilitators TAP cities of Talence, Pessac, Lille, ..., CDC Gates of inter-seas. Example of national action: Training of the digital mediators of the 8 Inria centers.
Partnership
The project is carried out in main collaboration with the LSRO Laboratory from EPFL (Lausanne) and others collaborations with French National Education/Rectorat d'Aquitaine, with Canopé Educational Network, with ESPE (teacher's school) Aquitaine, ESPE Martinique, ESPE Poitiers, National Directorate of Digital Education
Created pedagogical documents and resources
-
IniRobot pedagogical kit [94]: This pedagogical booklet provides activities scenarized as missions to do. A second pedagogical booklet has been also created by three pedagogical advisers for primary school, with pedagogical instructions and aims, under ou supervision. http://tice33.ac-bordeaux.fr/Ecolien/ASTEP/tabid/5953/language/fr-FR/Default.aspx A new pedagogical kit is in progress, Inirobot Scratch, which will propose activities with Scratch and Snap! and Thymio robot.
-
Inirobot website and forum http://www.inirobot.fr With this website, teachers, animators and general public can download documents, exchange about their use of inirobot' kit.
-
Publication about Inirobot and Poppy Education A poster and talk were produced in Didapro-Didastic 6 Conference in Namur (Belgium) on 2016 January. [99]
Scientific mediation
Inirobot is very popular and often presented in events (conferences, workshops, ...) by us and by others.
Symposium robotics
With Poppy Education, Inirobot is a main line in our colloquium "Robotics and Education" (http://dm1r.fr/colloque-robotique-education/)